Treating Neck Pain Without Surgery
The hip is essential for movement but can sustain damage over time, especially in active individuals. Injuries and wear can lead to pain and reduced mobility, requiring effective non-surgical treatment.

Cervical disc herniation, spinal stenosis, myofascial pain syndrome, and occipital neuralgia can lead to persistent pain, numbness, and mobility challenges due to nerve compression. These conditions often stem from spinal degeneration, injury, or nerve irritation. Unlike general muscle discomfort, they involve nerve-related dysfunction.
At Dr. Sonali’s clinic, advanced non-surgical treatments like PRP, prolotherapy, and laser therapy help reduce pain and restore mobility.
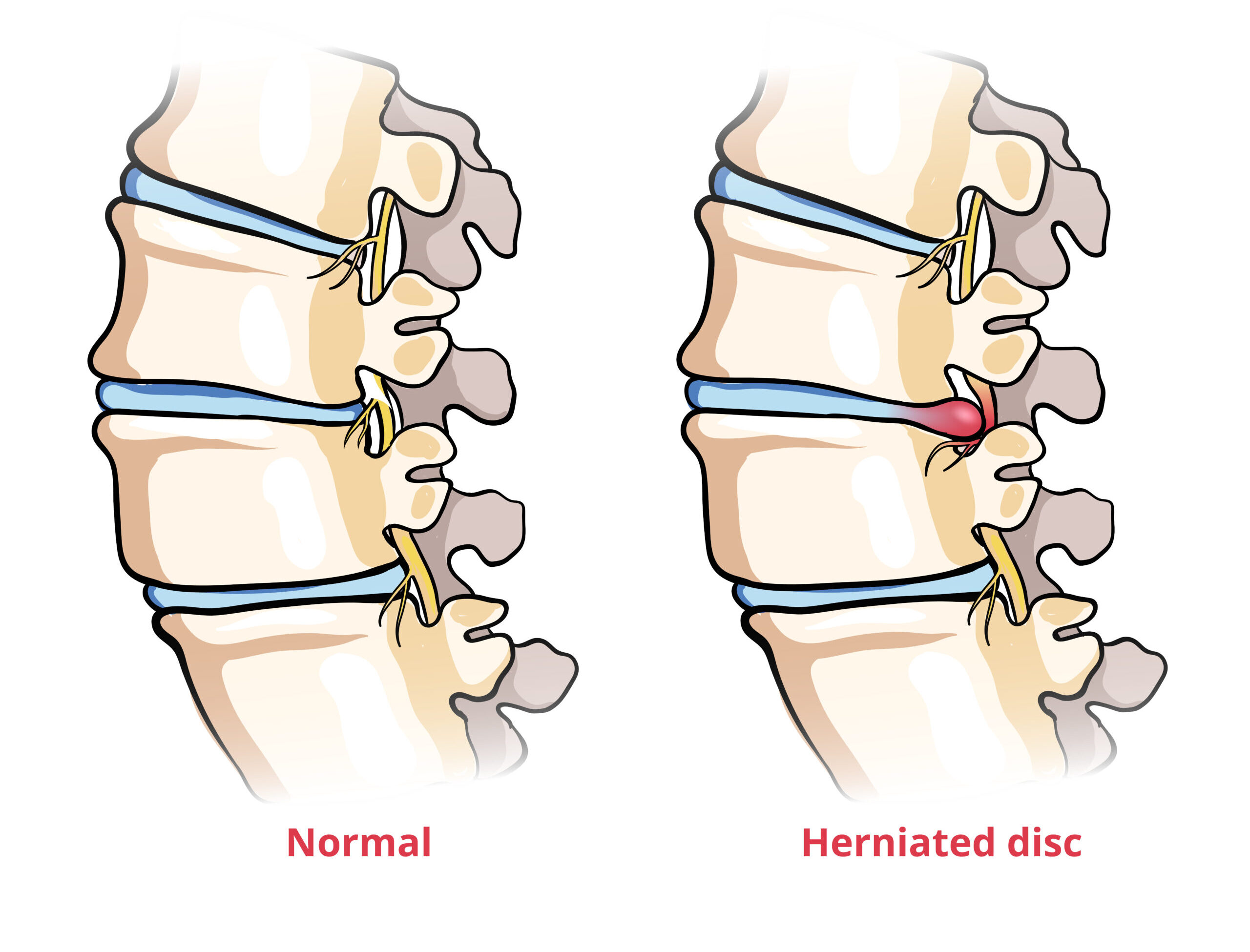
Disc Herniation
Causes:
Cervical disc herniation occurs when intervertebral discs in the neck region rupture or protrude beyond their normal boundaries, compressing nearby nerves. The cervical spine, comprising seven vertebrae (C1 to C7), contains shock-absorbing discs with a tough outer layer and a soft, gel-like center. Degradation of these discs due to aging, wear and tear, or external factors can lead to herniation.
Symptoms :
- Persistent neck pain
- Radiating pain, numbness, or tingling (Radiculopathy)
- Muscle weakness in shoulder, arm, or hand
- Reduced range of motion
- Recurring headaches
Diagnosis:
A comprehensive physical examination is crucial to identify the source and extent of disc herniation. Physicians typically employ advanced imaging techniques such as MRI and X-rays to visualize the intervertebral discs, assess nerve compression, and rule out alternative conditions. The diagnostic process aims to precisely locate the herniation and determine its impact on surrounding neural structures.
Cervical Stenosis
Causes :
The disorder known as cervical spinal stenosis is defined by the neck region’s spinal canal narrowing, which compresses the spinal cord and nerves. Degenerative changes in the spine brought on by aging are usually the cause of this progressive disorder. Cervical spinal stenosis is caused by a number of circumstances, such as underlying medical problems, structural changes to the spinal architecture, and natural aging processes.
Symptoms :
- Chronic neck pain
- Radiculopathy (radiating pain, numbness, or tingling)
- Difficulty walking and maintaining balance
- Loss of motor skills
- Weakness and numbness in extremities
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Potential loss of bowel and bladder function in severe cases
Diagnosis :
We use a detailed physical exam to assess reflexes, muscle strength, and nerve function. Advanced imaging like MRI, X-rays, and EMG helps pinpoint spinal narrowing, nerve compression, and structural changes.

Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Causes :
Myofascial pain syndrome is a chronic disorder characterized by heightened sensitivity in the body’s connective tissues. Triggered by specific muscular tension points, this condition causes localized and radiating pain through the fascia—the thin membrane surrounding muscles. Unlike temporary muscle aches, these trigger points generate persistent discomfort that can significantly impact mobility, posture, and overall physical well-being, creating a complex pain experience that disrupts daily functioning.
Symptoms :
- Persistent deep muscle pain that may radiate to different body areas
- Painful, tender muscular trigger points sensitive to compression
- Reduced movement range with associated stiffness and discomfort
- Muscle weakness and difficulty maintaining physical activities
- Referred pain experienced in regions distant from the original trigger point
Diagnosis :
Diagnosing myofascial pain syndrome involves a comprehensive medical evaluation, where clinicians identify trigger points, assess muscle function, and use diagnostic ultrasound. They carefully rule out alternative pain sources through targeted imaging and tests to develop an accurate understanding of the patient’s condition.

Occipital Neuralgia
Causes :
Lumbar and thoracic facet conditions affect the facet joints in the middle and lower back, which provide stability and facilitate spinal movement. Degeneration or deterioration of these joints leads to pain and other symptoms.
Symptoms :
- Ache in the back
- Difficulty bending or twisting
- Tightness around the affected area
- Discomfort spreading to limbs
- Worsens with standing or movement
Diagnosis :
Diagnosing facet disease requires a thorough clinical evaluation, including a physical examination to assess posture, mobility, and areas of discomfort, along with imaging studies such as MRI, CT scans, and X-rays to rule out other disorders and detect joint degeneration. Accurate diagnosis enables medical professionals to develop an effective treatment plan to alleviate symptoms and restore mobility.